Foreword by Mark Rejhon of Blur Busters:
This article is written a new guest writer, William Sokol Erhard, with some editing by Mark Rejhon. There will be additional pieces coming out. Let’s welcome William aboard!
Introduction
Advanced image temporal upscaling and latency compensation techniques are crucial for running super demanding pathtracing, allowing inputs to feel responsive in demanding applications, and especially in making AR and VR possible with current technology but how do they truly work?
This article will define and explain these common methods used to improve both temporal fidelity, reduce input latency, or both.
Interpolation is the process by which two (or more) discrete samples separated by space or time are used to calculate an intermediate sample estimation in an attempt to reproduce a higher resolution result.
Extrapolation is the process by which two (or more) discrete samples separated by space or time and used to calculate a predicted sample estimation outside the bounds of the existing samples in an attempt to expand those bounds.
Reprojection is the process by which an image is shown (often for a second time) in a spatially altered and potentially distorted manner using new input information to attempt to replicate a new image that would have taken that camera position input information into account.
Interpolation
Interpolation can be a complex and difficult feat when we’re talking about a high resolution rendered image but has been used at a much smaller scale in many disciplines for decades.
Since the hand-drawn days, animations have been based on established static images (keyframes) with inbetweens between that and the next keyframe. Those inbetweens are tweened by making small, progressive changes from those keyframes. Digital animations are built on the same principle and even when keyframes are procedurally generated and are set every 1/60th of a second, tweening is still used when the rendered result requires upscaling beyond that rate. Tweening is a form of interpolation.
In the case of an object moving in a straight line at a fixed velocity in the world, interpolating between two keyframes of an animation can be as simple as linearly calculating how far the target frame is from each of the two keyframes in time and doing a simple weighted average between them. That type of interpolation breaks down when you start moving on a curve or change velocity. Many mathematical functions can help create more flexible interpolations.


Credit: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interpolation
Sometimes simple calculations like a polynomial function are adequate, sometimes it makes sense to use only a polynomial function in a series of fixed range pieces that are called a spline. These interpolations work not just in one dimensional space but also two and three dimensions and beyond.
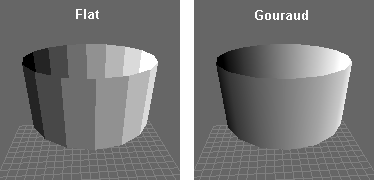
These types of interpolation are used all the way through the image rendering process in processes like shading. Using simple shading based on the vertices of a mesh without interpolation results in sharp changes of shading that show off every polygon. Even a simple linear interpolation of the shading values from each vertex allows the renderer to produce a smooth looking image without significantly reducing performance like increasing mesh polygon count would. This is known as Gouraud shading.
This simple interpolation still leaves some issues however. On the right sphere you can make out triangular artifacts that betray the low fidelity mesh. That can be resolved, again without reducing performance significantly by simply interpolating the information used to shade each pixel. This is known as Phong shading. The end result is a nearly flawless shade on a sphere or smooth object without the near infinite number of polygons that would be required to reproduce that result with brute force.

Credit: OpenOffice.org – Shading
Interactive Gouraud vs Phong Shading Demo from the University of Toronto.
Interpolation is used in image upscaling of all kinds and is known as bilinear, trilinear, or Lanczos filtering among many other more complex varieties.
In moving images like a movie or a video game interpolation can be done between each frame to result in more images and smoother motion. This is traditionally done by using computer vision, and optionally machine learning, in processes like block matching, corner detection, and optical flow. These methods find moving elements common to multiple frames and interpolate the difference between them. These methods still result in significant artifacts however when there are repeating patterns like a picket fence or some parts of the image move differently than other parts of the image like with parallax. All of these methods are prone to significant artifacts in large part because they are only operating in a 2 dimensional image that is, in actuality, representing a 3 dimensional environment. These types of interpolation are commonly integrated into television sets and (in part) produce what has been described as the “soap opera effect”.
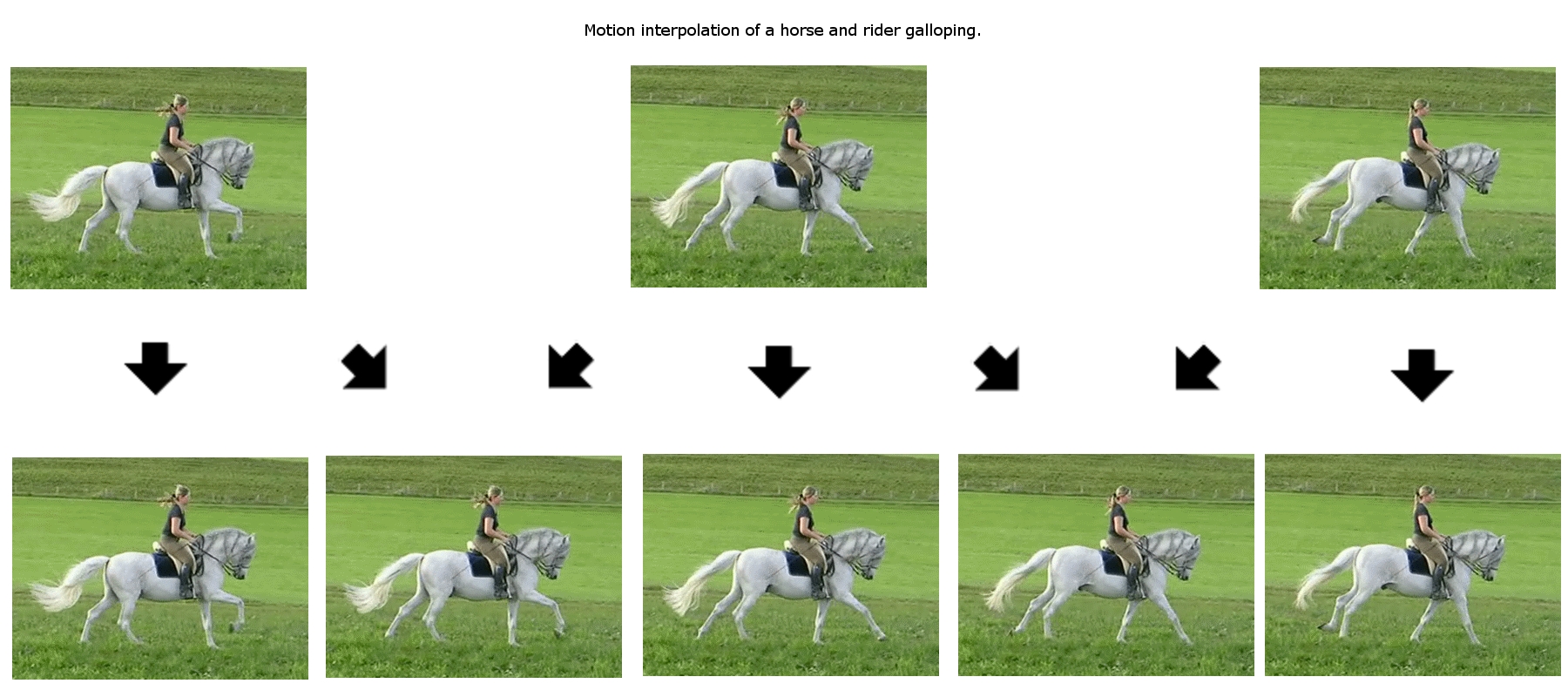
Credit: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_estimation

Credit: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parallax_scrolling
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_map
Depth aware video interpolation methods however are able to understand which parts of the image are moving nearer to the camera and which are further. They have access to that 3D understanding quite easily in video games by using motion vectors of every rendered object in the image as well as the generated depth map or “Z-buffer”. A simple combination of optical flow and motion vectors can be used to produce an effective interpolation with substantially fewer artifacts than traditional 2D screen space interpolation. Traditional computer vision but also machine learning can be effectively used to calculate depth maps of even live action video and use that information for depth aware interpolation as well.
Extrapolation
Extrapolation is for all intents and purposes the same as interpolation but instead of using multiple samples to produce an approximated intermediate sample inside that existing range, it uses that information to approximate a sample beyond the bounds of the input samples used. Both interpolation and extrapolation are forms of estimation based on multiple input samples.
The issue with extrapolation however, is that the predictions made are substantially less reliable than interpolated methods and can cause more substantial artifacts that overshoot the desired and succeeding value. One example of this overshoot is found in multiplayer video games when a character is rubber banding and is moved back because the server position for that player has not moved forward appropriately. Without extrapolation, the client would have to wait for the server to reflect the new position and the user would only move at that point. If, like in the case of rubber banding, the server doesn’t update the position, the user simply wouldn’t move.
Another example of overshoot is caused by LCD overdrive. This example is slightly more complex because the starting color and the target color are both known but the display must extrapolate from those values to derive a value beyond the target color and use its corresponding voltage on the pixel in question. That extrapolated value must correspond perfectly with the delay in LCD pixel response time or the display will either be left with a slow pixel response time or an overshoot of the color beyond the bounds of the two samples used to create that pixel transition.
Reprojection
Reprojection is probably the most interesting topic here. Regular projection, in the 3D graphics sense, is the method by which a 3D representation of something is converted into a 2D representation using a mathematical view. While there are oblique and orthographic projections like isometry, the most common and relevant projection is perspective. 3D graphical rendering uses a projection in the form of a virtual camera frustum to create a 2D array of pixels, known as a texture, that is shown on a display.
Reprojection is simply taking that texture, projecting it out into 3D space, moving the camera based on new inputs and rendering (only) that projected image again from the new perspective. This process is generally immensely faster to do than rendering a brand new frame from scratch.


Credit: patents.google.com/patent/US20150029218A1/en (Microsoft LSR)
Simple planar reprojection, like the diagrams above describe, is effective in accounting for camera rotation but falls flat for camera translation. Depth aware reprojection can use the z-buffer to compensate for some of the parallax effects caused by camera translation. Naturally, parts of the image that were occluded in the previous frame would not have any information to show in the new projection so gaps may occur in depth aware reprojection. Planar reprojection can be described as using three degrees of freedom (3DOF) while depth aware reprojection can be considered 6DOF. Realistically, reprojection by itself can only effectively compensate for camera movement.
In virtual reality, reprojection is used not only to compensate for dropped frames that could cause significant simulation sickness but they are also used every frame to reduce motion to pixel latency and therefore keep the virtual world in better alignment with the real world during head motion. This “always on” type of reprojection is called late stage reprojection because it occurs at the last possible moment before the image is drawn to the display in order to get the most recent input. Presumably for performance reasons, XR compositors generally use planar reprojection for late stage reprojection.
Reprojection can be used to output multiple displayed frames per real rendered frame but, without additional interpolation/extrapolation, raw reprojection will always result in multiple image crosstalk for any parts of the image not adjusted in that reprojection. The motion controllers in VR, other characters in the world, and the airplane flying by overhead will all be subject to the full latency and update rate of the native rendering plus potentially additional artifacts resulting from the reprojection.
That being said, Mark Rejhon has done several tests that can help experimenters reduce lots of artifacts seen during reprojection:
Reprojection as Lagless Blur-Reducing Frame Generation Techology to Replace Motion Blur Reduction Techologies (ULMB, DyAc, BFI, etc)
This chapter is an addendum mostly written by Mark Rejhon
It has long been said by Blur Busters that it is impossible to achieve 1ms MPRT strobelessly (without PWM or BFI) until crazy high 1000fps 1000Hz arrives.
The fantastic news is reprojection is sufficiently low-overhead to solve the 1000fps GPU problem with today’s highest-end GPUs — according to our tests. Reprojection makes possible “low-persistence via sample and hold” on today’s highest-end GPUs. There are now ways to make reprojection even reduce the input lag of the original frame rate, via genuine between-frame positional updates and input reads!
Also, on high-Hz fast-GtG display like OLED, 120fps vs 1000fps is the same motion blur difference as a SLR photograph 1/120sec vs 1/1000sec, as geometric frame rate and refresh rate differences produce dramatically visible motion blur differentials visible to average users, rather than just esports players. This is a way to bypass mostly useless refresh rate incrementalism (e.g. 240Hz vs 360Hz on slow-GtG displays), and provide benefits to more everyday users.
Comrade Stinger made a great reprojection demo, which LinusTechTips also covered. This reprojection demo is downloadable with an executable demo and source code on Google Drive. Here is the video:
The giant framerate increases that reprojection allows reprojection to be a motion blur reduction technology that may someday replace strobe-based motion blur reduction with strobeless motion blur reduction.
Reprojection can even rewind frametime latency into inputread latency. Some reprojection algorithms utilize inputreads and new positionals between original frames, to eliminate frame rendering latency. In tests of running this demo, we were able to achieve up to 1000fps frame rates from the demo, using only a few percent of a modern high-end GPU (via VSYNC OFF, even though our display is not capable of such refresh rates yet).
Although the graphics in the demo above is very rudimentary, most reprojection algorithms are scene-complexity-independent, which means the demo could very well be reprojecting Unreal Engine path-traced content, to similar frame rates. This means quadruple digit frame rates are possible near-term!
Reprojection Best Practices for Developers
This chapter was written by Mark Rejhon
We tested the reprojection demo. To make frame generation (e.g. reprojection) an esports-compatible lag-reducing frame generation technology that also reduces motion blur as well as strobe backlights, the following best-practices were discovered in 2023 by Mark Rejhon:
- To minimize artifacts, you need to use a high starting frame rate that is above flicker fusion threshold.
This makes all stutter vibrate so fast that it blends to display motion blur, like a fast-vibrating music string that looks blurry (TestUFO example, watch 2nd UFO for 30 seconds, where stutters blends to blur). Optionally, additional algorithms (e.g. ASW 2.0 or AI-based parallax-infilling) can be used to improve reprojection quality further, at some moderate cost to maximum frame rate multipliers possible. However, even without additional reprojection-enhancing algorithms (e.g. ASW 1.0 style), raising the starting pre-reprojection frame rate to 100fps+ hid most of the artifacts. - Faster-GtG higher-Hz displays benefit more from reprojection
Reprojection benefits all displays including LCD, but reprojection was particularly dramatic in improving motion quality on the new 240Hz OLED displays in experiments. You need a sufficient display refresh rate, since persistence (MPRT) on sample and hold is limited by the minimum refreshtime you can achieve. ~4ms MPRT requires 240fps 240Hz, and ~1ms MPRT requires 1000fps 1000Hz. - There are no double-image artifacts when reprojection is used on sample-and-hold
There are double image artifacts in virtual reality reprojection only because VR does flicker-based low persistence technologies. Instead, low-framerate objects simply has additional motion blur instead. In addition, as long as starting frame rate is above 100fps for all minimum frame rates of any object, stutters can disappear during framerate=Hz reprojection. Lower frame-rate components of the scene simply has more motion blur (e.g. enemy movements). In fact, some more advanced reprojection algorithms can can be reprojected too in the future (if integrated into the game engine)! - Reprojection goes lagless (and even lag-reducing) when rewinding rendertime latency to input-read latency.
Instead of lag-increasing interpolation, it is possible to have lag-reducing reprojection! To achieve this successfully, all visible frames must be reprojected, in order to undo rendering latency. To avoid jitters that can be amplified-visibility on low-MPRT displays, frames should be as reprojected as “game time”-accurate as possible, with between-frames “game times” synchronized to refresh cycles. See the diagram above. A slow frame (rendered in 10ms) can be morphed-ahead to newer frame (only 1ms behind input reads). Some reprojection algorithms can even move additional positionals (e.g. move enemy positions by modifying an old frame) between original rendered frames. A simpler 1000fps reprojection algorithm only need less than 25% of a top-of-the-line GPU, to achieve frame rates useful for tomorrow’s 1000Hz displays. - Frame generation at large frame rate multipliers (8x+ frame rate) can replace other motion blur reduction technologies (e.g. BFI, ULMB, DyAc, etc).
This is a fully ergonomic flicker-free method of display motion blur reduction. No PWM or flicker. Display motion blur reduction is achieved via brute frame rates and refresh rates. Increasing frame raters by 10x frame rates reduces display motion blur by 90%. The MPRT of sample-and-hold is throttled by minimum frametime (refreshtime), so a higher frame rate and refresh rate lowers the MPRT persistence. The use of quadruple-digit frame rates and refresh rates is sufficient to outperform most strobe backlights, when used on a near-0ms-GtG display technology. With large-ratio frame generation via reprojection, strobe backlights (and their flicker eyestrain) could potentially become obsolete for modern content! - GPU motion blur effects should still be optionally provided as a defacto accessibility option
Some people hate stroboscopic effects of finite frame rates (another potential eyestrain factor), even more than display motion blur or low frame rates. Fortunately, ultra-high frame rates (e.g. 1000fps) require only one frametime or less (e.g. 1ms) of intentional GPU motion blur effect. So at ultra high frame rates (1000fps) vastly less GPU blur effect is necessary in order to eliminate stroboscopics (phantom array effect). For many, this would be almost an undetectable re-increase in motion blur, but a massive decrease in stroboscopic effects. People who get motion sick from both stroboscopics and motion blur, are sometimes completely unable to play a game nor use VR today. Using reprojection + an extremely tiny bit of GPU blur would miraculously solve both at the same time. No stroboscopics, no blur, no flicker, no strobe backlight, no BFI — motion would be much closer to analog framerateless real life!
Having (Blurless) Cake and Eating It (Strobeless) Too.
Consequently, large-multiplier reprojection reduces enough display motion blur to make strobing obsolete well before the end of this decade for PC-based and VR-based content. This is big — an ergonomic strobeless method of motion blur reduction. All all VR vendors use flicker-based motion blur reduction, which not every eyes can handle. This would make gaming and VR even more motion-friendly. Even Apple is forced to flicker their Vision Pro headset to reduce display motion blur, as a method of display motion blur reduction, and not everyone can handle flicker (PWM).
Reprojection to quadruple-digits allows everybody to have cake and eat it too — blurless and strobless. In fact, NVIDIA even cited our TestUFO as part of a research paper, Temporally Dense Raytracing (Page 2). Be noted, reprojection is mostly a GPU-agnostic technology,
While the general outline of reprojection principles are not exclusive to a specific GPU vendor, reprojection can still be customized by GPU vendors (e.g. AI or neural silicon for improved infill of parallax-reveals and reprojection of enemy movements) and branded as such (FSR, XeSS, DLSS, etc). Reprojection can be used with both traditional triangle-rendering and pure raytracing algorithms, so reprojection methodologies is a fairly universal way to massively reduce the cost of rendering a brand new frame.
For simple reprojection algorithms, only a few percent of the latest GPUs need to be utilized to multiply a frame rate dramatically by 4x to 10x+. This reduces display motion blur quite noticebly, by a factor of 4x-10x. This means BFI and strobing can become obsolete for modern content such as PC-based gaming.
Linus Tech Tips cover reprojection as a way to reduce costs for end users.
However, we view reprojection as a revenues-increaser for GPU companies since good reprojection looks like GSYNC, ULMB, DLSS combined, at esports-friendly input latencies!
- Better than GSYNC, since reprojection can ensure framerate=Hz.
- Better than ULMB, since reprojection can reduce display motion blur.
- Better than DLSS, since reprojection is a frame generation technology.
- Lagless, if reprojection algorithm utilizes between-frame input & positional updates.
- Ergonomic flicker-free & PWM-free.
Therefore, it is a potential Holy Grail frame generation technology, as a replacement for BFI and strobe backlights for modern content, while still being able to use full advanced features such as path traced graphics.
We still need high-end GPUs to do the scene complexities needed, and powerful reprojection engines capable of frame rates necessary to achieve this potential Holy Grail. Therefore, high end users will purchase even more high end GPUs, in order to achieve this Holy Grail. And the benefits are more massively visible to end users because of the simultaneous benefits.
More Human Visible Benefits to Resurrect Sales of GPU and Displays
This could help resurrect high-end GPU sales (RTX 4090) as there has been a slowdown in GPU sales, and since 240fps+ is no longer just for esports. Even ergonomic motion blur reduction 1000fps can benefit the mainstream, if it’s a ‘free’ feature like 720p vs 4K is now almost the same cost in TVs.
Imagine playing Cyberpunk 2077 Ultra Detail with path-traced graphics at 240 frames per second on today’s top-end GPUs, if CD Projekt Red incorporates elements of the existing reprojection source code into the game engine! 480 Hz and 1000 Hz OLEDs are also expected to arrive on the market before the end of this decade, which would require reprojection for Ultra-detail league raytraced graphics to maintain framerate=Hz.
However, large-multiplier reprojection should be introduced more quickly due to very effective benefits on current 240Hz OLEDs already hitting the market at the time of this writing, and resurrect more interest in PC gaming and reduce VR headaches by the flicker-sensitive.
In fact, in our tests, even 1000fps reprojection is now achievable on today’s latest GPUs, so we now implore OLED and MicroLED developers to more quickly develop 1000fps 1000Hz “0ms GtG” display technologies, since it would make possible 4K 1000fps 1000Hz Unreal Engine path-traced picture quality possible before the end of this decade — at esports-friendly input latencies!
Frame rate upgrades need to be geometric (2x to 4x). Due to the diminishing returns of the refresh rate race, frame rate and refresh rate upgrades need to be geometric (such as 60 -> 144 -> 360 -> 1000) to be noticeable to casual gamers on near-0ms-GtG technologies. 240fps vs 1000fps at framerate=Hz on flickerless displays — is a more human-noticeable 4x difference in display motion blur, than 144fps vs 240fps. Larger numbers of casual users will notice the motion blur reduction benefits. Users are losing interest without geometric frame rate upgrades necessary for dramatic motion-quality improvements on ray traced content.
We need to introduce triple-digit and quadruple-digit frame rates and refresh rates in display, gaming and GPU market beyond esports, and we can’t do it with mere frame rate incrementalism or eye-killing strobe technologies. It will be easier to say goodbye to low frame rates (30fps) on gaming consoles, and increase detail of 60fps and 120fps on PlayStation and XBox too, if we used improved reprojection algorithms along with the Developer Best Practices above.
Good reprojection requires between-frame positional updates (input reads, enemy positions), to help morph previous rendered frames to new frames in a lagless manner:
- Game engine vendors (Unreal Engine and Unity Engine) should add early reprojection support.
- GPU vendors (AMD, Intel and NVIDIA) should add reprojection to FSR, XeSS and DLSS frame generation APIs.
- Graphics API vendors (Vulkan) may wish to investigate adding possible paths to adding frame generation helper APIs.
While simple reprojection algorithms may only affect mouselook/strafe, there are research in future advanced reprojection algorithms capable of updating important positionals (e.g. enemy positions)
We now have displays (240Hz OLEDs) that badly need this technology. Technology could resurrect sales of GPUs and displays, because of highly visible humankind benefits.
Conclusion
Frame generation technologies are here to stay, as they go more lagless and artifactless over time. Even Netflix can be considered as 23 fake frames per second and 1 real frame per second, due to prediction/interpolation math built into video compression standards including all the MPEG and H.26X standards.
Naturally, interpolation and extrapolation can also be used in conjunction with reprojection to mitigate the issues described before. Motion vectors and z-buffers can be used effectively in the estimation of moving elements in the environment. Neural networks and other advanced technologies can infill data from parallax reveals, with any frame generation technology, including reprojection. One can extrapolate the state of the image forward to the estimated time the final frame will be displayed then use camera position information to reproject that extrapolated image providing all the benefits of both extrapolation and reprojection simultaneously.
These methods are also capable of working effectively in regular 2D display games and applications as well. Interpolation is being used in realtime rendering by Nvidia’s Optical Multi Frame Generation (in DLSS 3.0) and reprojection has been demoed in a mouse input application by Comrade Stinger, in addition to many VR frameworks (e.g. Meta/Oculus ASW 2.0).
Many of these approaches require minimal involvement from the actual 3D engine or application so it’s fair to expect widespread support in the future.
It’s also foreseeable that the 3D engines (Unreal, Unity) and APIs (Vulkan, DirectX) themselves will adopt framerate generation technologies that access much more granular information tuned for the needs of that specific application. Including between-frame positional updates, can allow frame generation to become lagless.
However they are implemented, some combination of these techniques will be crucial to increasing temporal fidelity and reducing latency to the limits of human perception without unobtainable brute force processing power.
Related Blur Busters Articles
- Frame Rate Amplification Technologies
- Blur Busters Law: The Amazing Journey To Future 1000 Hz Displays
- Stroboscopic Effect of Finite Frame Rates
External Links
- Bézier Curves (splines):
youtu.be/aVwxzDHniEw - Video motion encoding:
developer.nvidia.com/blog/av1-encoding-and-fruc-video-performance-boosts-and-higher-fidelity-on-the-nvidia-ada-architecture/ - Regular reprojection and basic interpolation:
forums.flightsimulator.com/t/motion-reprojection-explained/548659 - Late stage reprojection:
learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/remote-rendering/overview/features/late-stage-reprojection - Comrade Stinger’s Reprojection:
youtube.com/watch?v=f8piCZz0p-Y - Linus Tech Tips on Reprojection:
youtube.com/watch?v=IvqrlgKuowE